U of M is a private, faith-based university that is home to nearly 4,000 students.
Anticipated degree:
Masters of Science in Nursing and Healthcare Informatics.
Total academic credits for this program are 38, and students must complete 385 experiential hours.
Required Courses with Course Descriptions


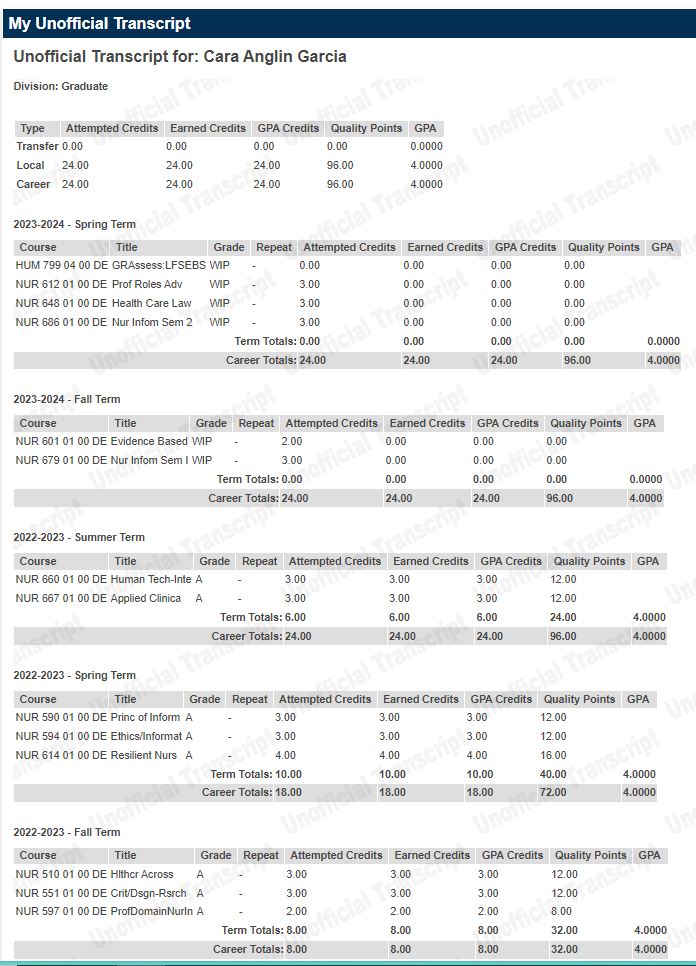
Unofficial Transcripts

Graduate Clinical Experiences
My clinical experiences ranged from acute care to ambulatory care centers, and allowed me to gain exposure to levels of leadership I hadn’t even encountered as a mid-level hospital manager. Being a student and assuring my preceptors that I was eager to learn from them seemed to fill them with an equal eagerness to share and impart wisdom and knowledge. These experiences have helped me to appreciate some of the complexities involved in clinical leadership, and have given me confidence, as my comprehension of many areas of leadership has been deeply enhanced. I feel that I am far more prepared to answer questions and participate in think-tank discussions with colleagues, superiors, and new employment partners.
The Essentials of Master's Education in Nursing
Essential I.
Background for Practice from Sciences and Humanities:
Recognizes that the master’s-prepared nurse integrates scientific findings from nursing, biopsychosocial fields, genetics, public health, quality improvement, and organizational sciences for the continual improvement of nursing care across diverse settings.
Essential II.
Organizational and Systems Leadership:
Recognizes that organizational and systems leadership are critical to the
promotion of high quality and safe patient care. Leadership skills are
needed that emphasize ethical and critical decision making, effective
working relationships, and a systems-perspective.
Essential VIII.
Clinical Prevention and Population Health for Improving Health:
Recognizes that the master’s-prepared nurse applies and integrates broad,
organizational, client-centered, and culturally appropriate concepts in the
planning, delivery, management, and evaluation of evidence-based clinical
prevention and population care and services to individuals, families, and
aggregates/identified populations.
Essential IX.
Master’s-Level Nursing Practice:
Recognizes that nursing practice, at the master’s level, is broadly defined
as any form of nursing intervention that influences healthcare outcomes
for individuals, populations, or systems. Master’s-level nursing graduates must have an advanced level of understanding of nursing and relevant sciences as well as the ability to integrate this knowledge into practice. Nursing practice interventions include both direct and indirect care components.









